Backup Plan Explained
Backup Plan
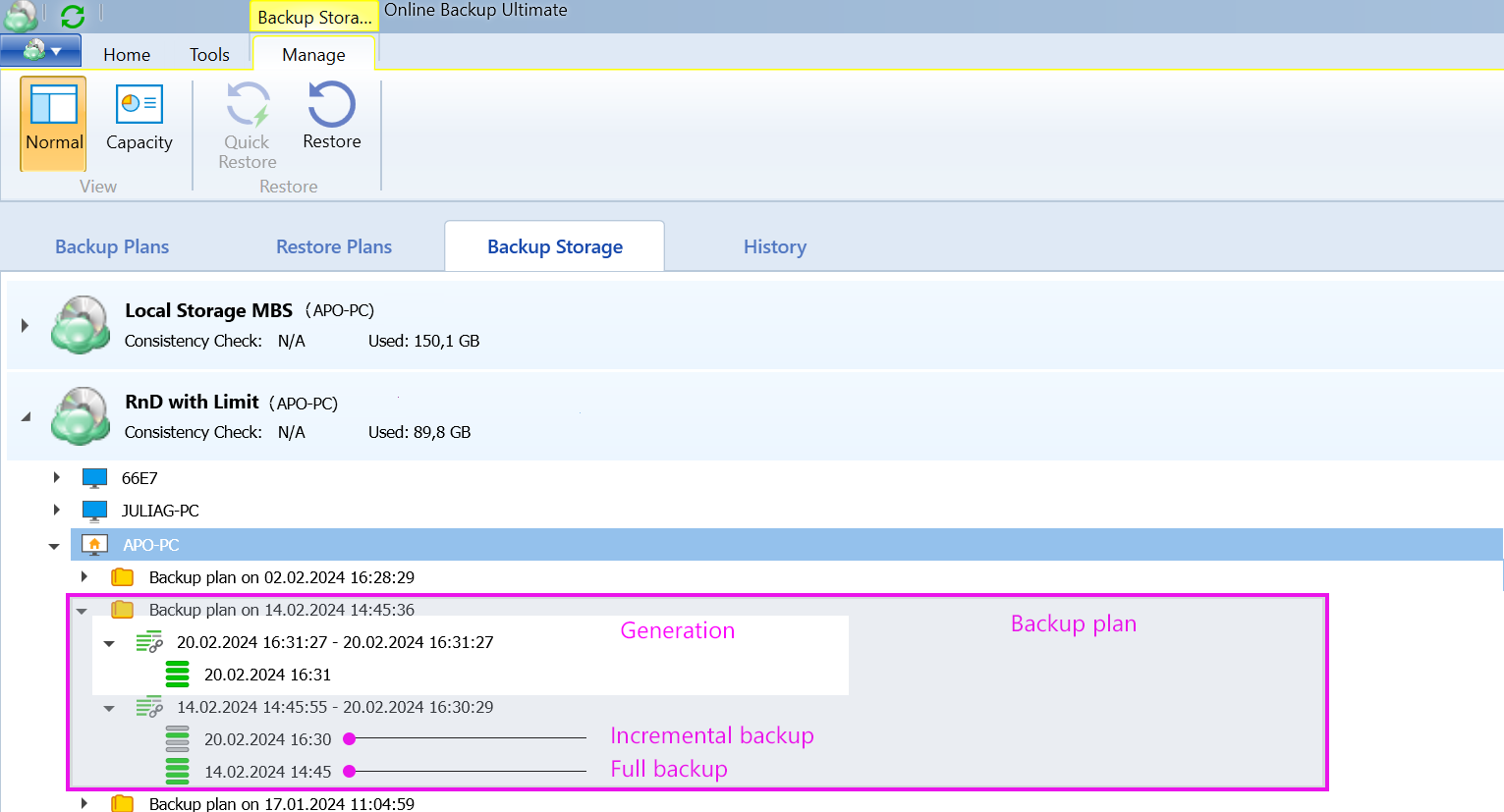
Managed Backup enables you to store the configuration of each backup you create so that you can run it at any time either manually, or on schedule. This configuration is stored as a backup plan, which you can create using the Backup Wizard.
Once a backup plan is configured, you can locate it in the Management Console on Computers. Click on the computer for which you want to see the backup plan,then on the side panel open the Backup Plan tab, and expand the backup storage to see backup plans stored in it.
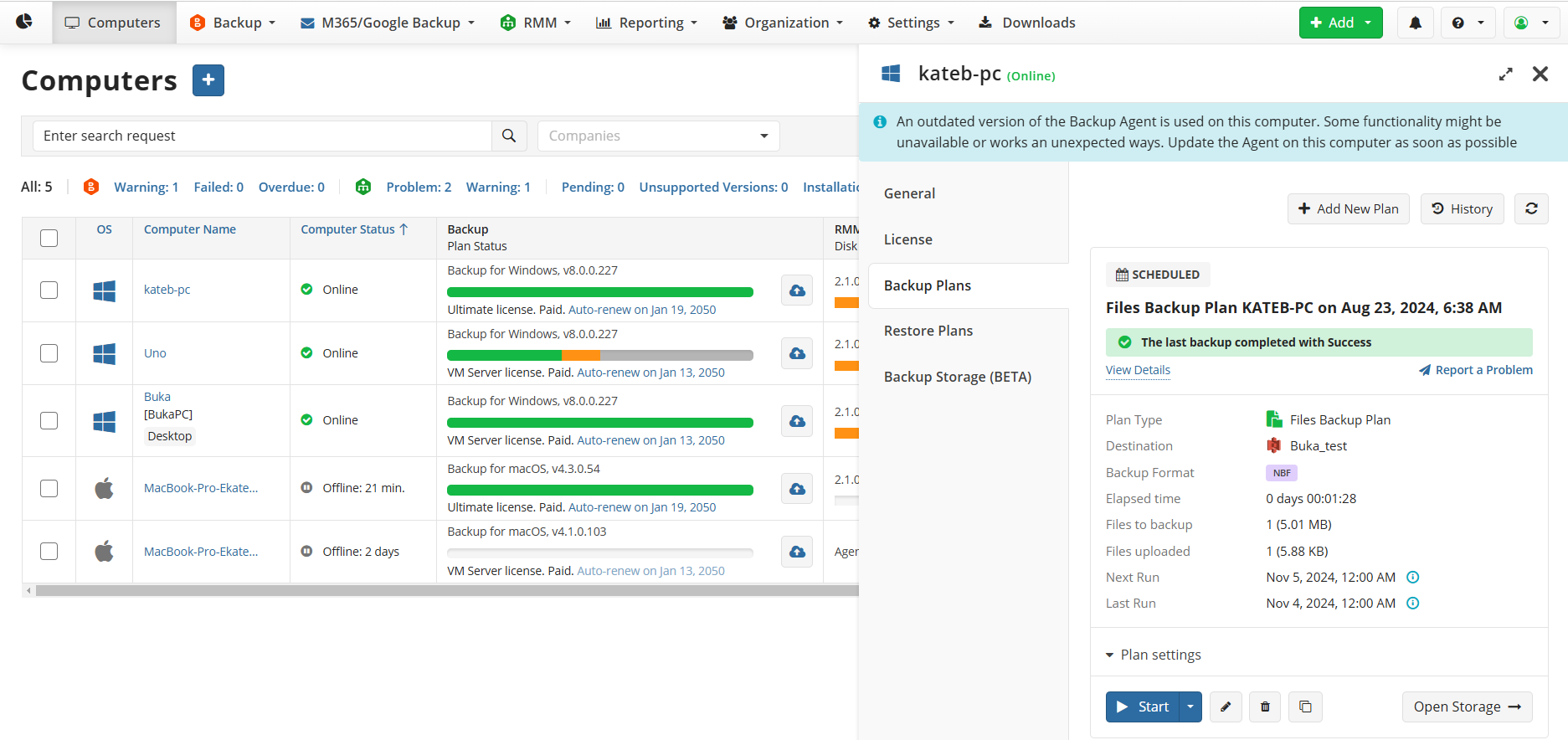
Backup plan status can be monitored on the plan tile.
You can also see the backup plan directly on the computer, on the Backup Plans tab of your Backup application.
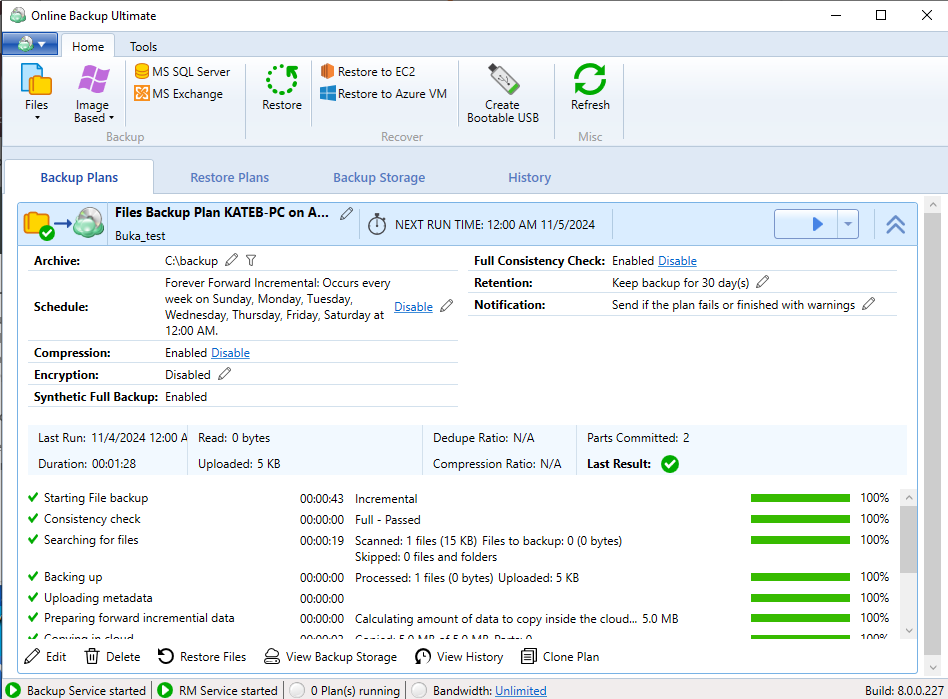
Full Backup
The first backup is always a full backup. Full backup is a copy of the entire dataset selected to back up. Once you run a full backup, the selected data will be sent to the backup storage. Running only full backups each time results in extra storage costs you can avoid using incremental backups. Full backup takes more storage space and time to complete than other backup types. That increases network and bandwidth load in the event of an offsite backup.
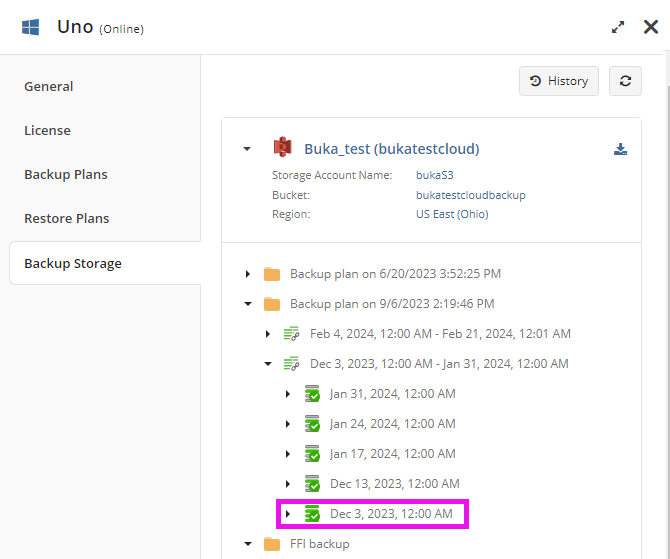
Synthetic Full Backup
Synthetic full backup is a type of full backup that makes a comparison to the previously backed up data on the storage and uploads only modified blocks of data from source to a backup storage. Synthetic full backup helps to reduce the amount of data uploaded and accelerates a full backup creation. Synthetic full backup requires in-cloud copying allowed in your backup storage destination.
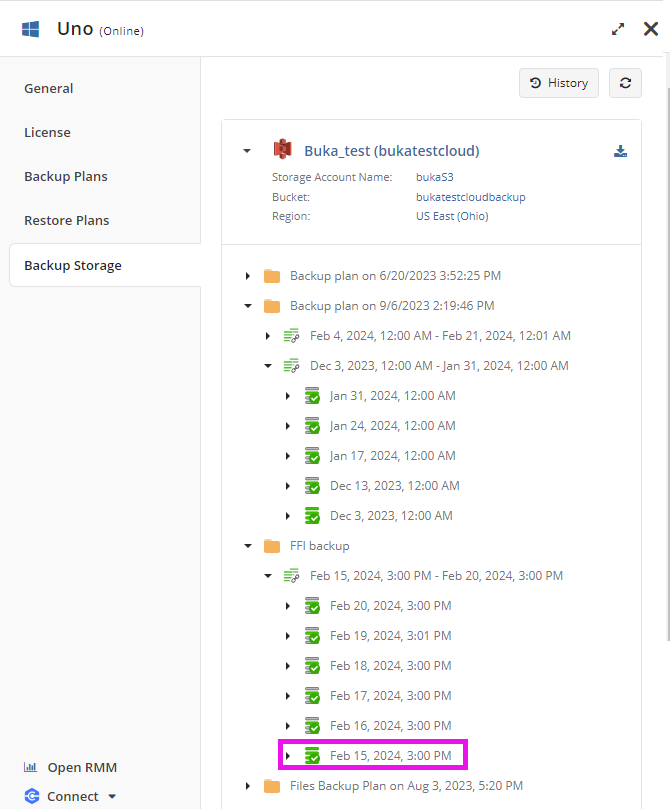
On the Backup Storage plan there is no visual difference between full backup and synthetic full backup.
Incremental Backup
An incremental backup is a type of backup that copies only data that was changed since the previous backup. Unlike a full backup where all dataset is copied to the backup storage with every backup job, the incremental approach allows you to perform a full backup only once in a while. Every next backup will include only files that were changed since the most recent backup.
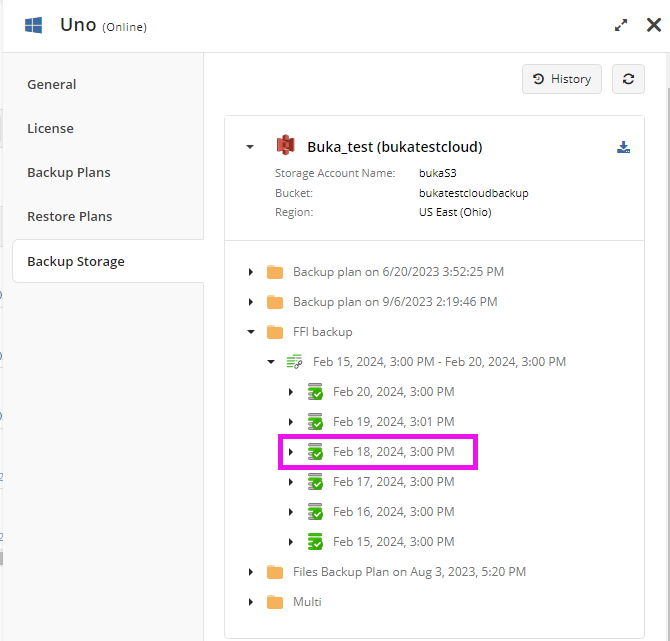
Restore Point
Restore Point is a partial data set for restore. A full-fledged restore point contains at least one file or directory.
If a restore point does not contain any file or directory, it is considered empty, but successful can contain blocks for further subsequent runs. A valid Restore Point guarantees a correct restore of backed-up data.
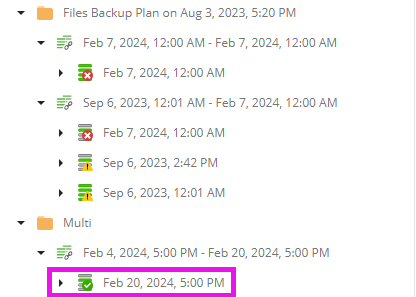
On the other hand, an invalid Restore Point does not contain a complete data set for restore, but at the same time can contain blocks that are used for restore from other Restore Points.
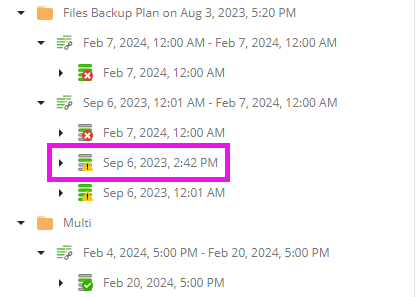
In case the backup plan failed, this backup plan run cannot be considered as a restore point.

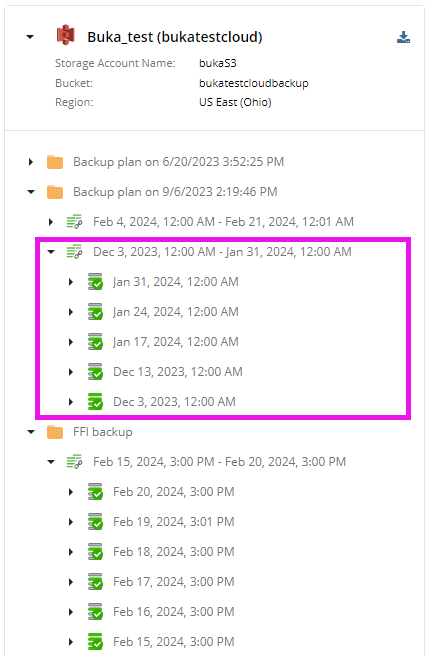
Generation
Generation is a complete self-contained dataset that is sufficient for restoration. In other words, generation is a sequence of a full backup and incremental backups for a specific backup plan. Every full backup starts a new generation.
Management Console:
Backup Agent:
In the new backup format, the retention policy is applied to generations, except the current one.